Multi-agent simulation : cellular automaton and boids (Java)
Contributors: Mathieu Tillet, Aymeric Lhullier
This project was part of the Object-Oriented Programming course.
The aim was to develop in Java an application for graphically simulating multi-agent systems.
Simulated systems included three systems of the cellular automaton type:
- Conway’s game of life
- Immigration game
- Schelling’s segregation model
Another simulated system was a self-organized swarm movement system: the Boids model.
Click the image to see a small demo of the result:
I was responsible for:
- Global class structuring of the project
- Event manager : update rate, boid death’s…
- Schelling’s segregation model implementation
- Wolf boid AI
Cellular automatons
Each cellular automaton implemented follows specific update rules but share the remaining implementation thanks to inheritance.
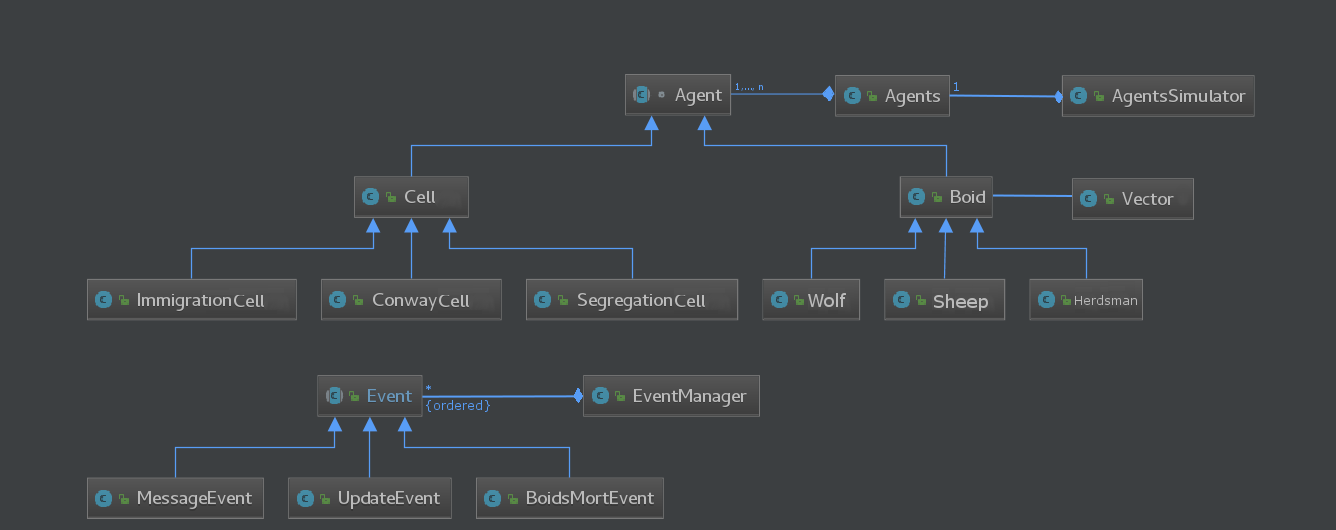
Boids
The Boids model is a flocking simulation model. Each agent is subject to at least two constraints :
- Neighboor effect : depending on their proximity, neighboors of the same specie attract or repel (if too close) each other.
- Screen encasing : borders of the screen repel the boids so as they stay visible during the simulation.
Specific species of boids were created, with customized behaviours :
- Wolves (in red) : wolves tend to hunt together, are pretty fast, are attracted to sheeps and afraid of herdsmen.
- Sheeps (in blue) : sheeps like to stay in big herds and regroup behind herdsmen. They are afraid of wolves but slower than them.
- Herdsmen (in green) : herdsmen try to protect sheeps from wolves. They can kill nearby wolves but are much slower than the other boids.